Passwordless authentication appears to be the new belle of the ball amongst tech experts. Of course, the reasons all bother on the general challenges experienced by security companies and businesses.
The security and tech world continue to advance in scope and sphere – through developing efforts to improve existing structure. These changes are prompted by the ongoing surge in security breaches in which no industry is spared.
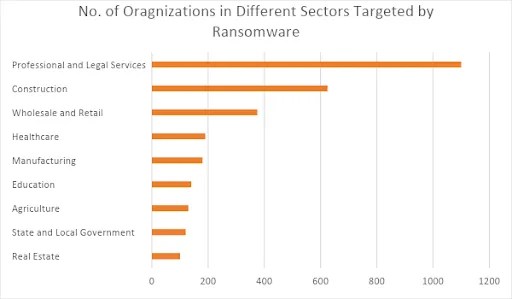
Security issues surrounding weak passwords serve as a driving factor for these breaches — and a nightmare for IT departments. As secure as some might believe them to be,, passwords remain the weakest link in today’s workplace security network. Stolen credentials are costly to resolve and come with many negative impacts.
As organizations rethink the future of the workspace, passwordless authentication seems to be a way out.
What is Passwordless Authentication?
Passwordless authentication is any method that eliminates the reliance on passwords to provide a a smoother user experience, stronger security posture, and reduced costs.
Passwordless authentication uses methods of identity proof to replace the use of passwords, passphrases, and other shared secrets. The replacements take OTPs as an alternate means. Authenticator apps, biometrics, hardware, and software tokens make up other forms.
Businesses encourage the adoption of passwordless authentication because it removes all vulnerabilities associated with secret-based passwords. But, there’s a constraint – the market is not fully ready for its adoption. Business enterprises struggle to cover the various use cases with a single solution.
Challenges of Password Authentication
Security Limitations
Passwordless authentication is not entirely foolproof, although it’s better than a password. Hackers can use malware to intercept one-time passwords. They also insert trojans into a browser to gain access.
Costs of Deployment
The implementation of passwordless authentication requires high costs. It comes with new software, hardware, trained employees, and more. Passwordless authentication also entails a change in management plans and projects.
The deployment also comes with hardware installations and the purchase of gadgets. In addition, the choice of software comes with hidden costs, software administration, maintenance, and migration.
Passwordless Authentication Methods
Biometric Authentication
It is a method that requires using biological characteristics such as facial features and fingerprints. This authentication method allows users to instantly log into their devices .
One-Time Passcodes (OTP)/PIN
The OTP is a method that puts the responsibility of generating dynamic codes on the service provider. As a result, it eliminates having to remember passwords or downloading apps.
Foremost in this category is the time-based one-time password (TOTP). The TOTP is a transient method and must be in sync with the time zone. It works with algorithms that generate passwords on a server and client whenever there’s system authentication. A major drawback is that a user may mistakenly tap multiple times to generate a token. When this happens, they have to restart the process.
Push Notifications Authentication
Push notifications work with an installed app on the user’s phone. The user receives a notification on a registered device containing the logins date, time, and location that allows them to accept or deny access.
Magic Links Login Authentication
Magic links require a user to enter an email address into the login box. An email is then sent with a link that requires clicking to log in. A user receives this magical link to ensure safety whenever there’s a login.
The Benefits of Passwordless Authentication
Reduced Costs
Password management and storage require a lot of resources. Resetting passwords and frequently changing password storage laws are also costly. Passwordless authentication helps to remove long-term costs.
Stronger Cybersecurity Posture
Passwords no longer provide a stalwart defense as many people repeat them multiple times.
Once a password gets breached, leaked, or stolen, it’s much easier for s hacker to gain access to your other applications. This allows malicious actors to then commit financial fraud or sell trade secrets to rival companies. Passwordless authentication takes care of these challenges by offering protection against the most prevalent cyberattacks.
Better User Experience and Greater Productivity
Users often have to generate and memorize multiple passwords, and because of this they sometimes forget them, forcing the task of then resetting them. For this reason, users use simple and uncomplicated passwords, Often using the same ones for numerous applications, with an addition of an extra character. The challenge here is that hackers find it easy to access these accounts.
Passwordless authentication eliminates these challenges, as users do not have to create or memorize their passwords. Instead, they only authenticate using emails, phones, or biometrics.
Scalability
Passwordless solutions work with technology and factors that end users already possess. Therefore, it becomes easier for mobile devices and laptops to infuse the various methods. Some passwordless authentication easily integrated includes biometrics and authenticator apps, Windows Hello, and fingerprints.
Top 10 Use Cases of Passwordless Authentication
Passwordless authentication can apply to a variety of use cases including:
- Customer payments authentication
- Remote logins
- Logins for financial services
- Call center authentication
- Personal logins
- Customer balance access
- Record access
- Mobile banking
- Wire transfers
- Push notifications
Changing the Security Paradigm: The Big Step
Businesses that integrate passwordless authentication have a strong concern for security. Organizations now realize that many security breaches result from the use of passwords. For them, the one-time cost of implementing passwordless authentication is more rewarding.
While it’s true that passwords are still quite common, the security risks are enough reason to make a switch. With the technology quickly gaining traction, there’s no better time to integrate passwordless authentication.
Indeed, passwordless authentication is the next digital breakthrough that offers key advantages over the traditional password including:
- It helps to lower costs while also increasing revenue. Customers tend to gravitate towards such products and services that provide trust and security.
- Providing a smooth user experience is preferrable to any customer.
- The presence of the technology and its adoption is a vital element for trusted security.
Nonetheless, passwordless authentication remains in its early stages. While many businesses have yet to adopt the technology, there’s a strong sentiment that its adoption will help change the face of security in the near-term.
About Version 2 Digital
Version 2 Digital is one of the most dynamic IT companies in Asia. The company distributes a wide range of IT products across various areas including cyber security, cloud, data protection, end points, infrastructures, system monitoring, storage, networking, business productivity and communication products.
Through an extensive network of channels, point of sales, resellers, and partnership companies, Version 2 offers quality products and services which are highly acclaimed in the market. Its customers cover a wide spectrum which include Global 1000 enterprises, regional listed companies, different vertical industries, public utilities, Government, a vast number of successful SMEs, and consumers in various Asian cities.
About Portnox
Portnox provides simple-to-deploy, operate and maintain network access control, security and visibility solutions. Portnox software can be deployed on-premises, as a cloud-delivered service, or in hybrid mode. It is agentless and vendor-agnostic, allowing organizations to maximize their existing network and cybersecurity investments. Hundreds of enterprises around the world rely on Portnox for network visibility, cybersecurity policy enforcement and regulatory compliance. The company has been recognized for its innovations by Info Security Products Guide, Cyber Security Excellence Awards, IoT Innovator Awards, Computing Security Awards, Best of Interop ITX and Cyber Defense Magazine. Portnox has offices in the U.S., Europe and Asia. For information visit http://www.portnox.com, and follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn.。